1. Introduction
Just 24 hours ago, the U.S. Department of Commerce announced new export controls on high-purity titanium metal powder due to its strategic importance in aerospace and defense additive manufacturing—a move that’s already rippling through global supply chains. This underscores how critical titanium powder has become in advanced industries. Whether you’re an engineer, a procurement specialist, or a hobbyist exploring metal 3D printing, understanding titanium powder—from its forms and functions to its fluctuating price—is essential.

Titanium powder isn’t just one material; it’s a family of engineered powders with distinct properties tailored for specific applications. From pure titanium powder used in biomedical implants to specialized alloys like Ti6Al4V (also known as Ti64) for jet engines, the versatility of this material is unmatched among lightweight metals.
2. What Is Titanium Powder?
Titanium powder refers to finely divided particles of titanium metal or its compounds, typically ranging from nanometers to hundreds of microns in size. It can be produced in various morphologies—spherical, irregular, or flake-like—depending on the manufacturing method. Common types include gas atomized titanium powder (ideal for 3D printing due to its spherical shape and flowability) and HDH (Hydride-Dehydride) titanium powder, which is more angular and cost-effective for pressing and sintering.
Beyond elemental titanium, the term often encompasses related materials like titanium dioxide (TiO2) powder—a white pigment used in paints, sunscreens, and food—and advanced ceramics such as titanium carbide powder, titanium nitride powder, and titanium diboride (TiB2) powder, all valued for extreme hardness and thermal stability.
3. Key Types and Their Uses
Pure titanium powder is widely used in chemical processing and medical devices thanks to its biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Meanwhile, titanium alloy powder—especially Ti6Al4V powder—is the gold standard for aerospace and automotive 3D printing. Its strength-to-weight ratio and performance at high temperatures make it indispensable.
Other niche variants include titanium flash powder (used in pyrotechnics, though highly reactive), titanium nanopowder for catalysis, and even titanium-coated diamond powder for ultra-precise polishing. TiH2 powder (titanium hydride) serves as a foaming agent in metal matrix composites, while burnt titanium powder coat refers to oxidized residues sometimes seen in thermal spray processes.

It’s also worth noting that ‘titanium dust’ is an informal term often used interchangeably with fine titanium powder—but in industrial safety contexts, it highlights the fire and explosion risks associated with airborne metal particles.
4. Titanium Powder for 3D Printing: The Game Changer
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized how we use titanium. Titanium powder for 3D printing—particularly spherical, gas-atomized grades—enables the production of complex, lightweight parts impossible with traditional machining. Industries from dentistry to space exploration rely on titanium 3D printing powder to create custom implants, rocket nozzles, and turbine blades.
The demand has driven innovation in powder recycling and quality control. However, cost remains a barrier: titanium powder for 3D printing price typically ranges from $300 to $800 per kg, depending on purity, particle size distribution, and alloy type. For example, Ti6Al4V powder price sits higher than pure titanium powder due to added vanadium and aluminum content.
5. Pricing and Sourcing Considerations
When you look up titanium powder price per kg, expect significant variation. Factors include production method (gas atomized vs. HDH), oxygen content, certification (e.g., ASTM standards), and volume. International titanium powder markets are volatile—geopolitical tensions and energy costs directly impact titanium metal powder price.
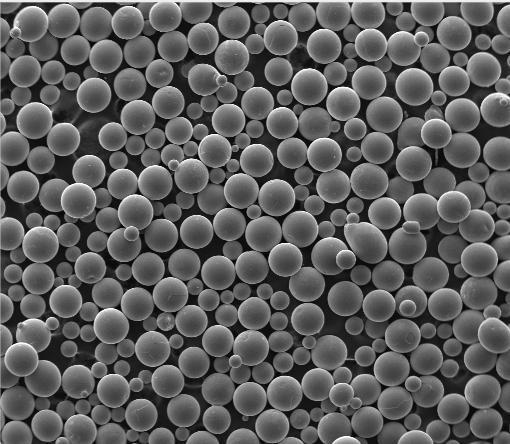
To buy titanium powder reliably, work with a reputable titanium powder supplier who provides certificates of analysis. Beware of misleading listings: some vendors advertise ‘titanium powder’ but actually sell TiO2 nano powder, which is chemically inert and unsuitable for metallurgy. Always clarify whether you need metallic or oxide forms.
6. Related Advanced Metal Powders: Molybdenum and Tungsten
While titanium dominates lightweight applications, molybdenum powder and tungsten powder serve complementary roles in high-temperature and wear-resistant environments. Molybdenum metal powder (often called moly powder) is used in furnace components, while molybdenum disulfide powder (MoS2 powder) acts as a dry lubricant—sometimes sold as ‘dry moly powder.’ Other variants include ferro molybdenum powder for steelmaking and TZM powder (a molybdenum alloy) for aerospace.
Similarly, tungsten powder—also known as wolfram powder—is prized for its density (19.25 g/cm³) and melting point. Pure tungsten powder and spherical tungsten powder are used in radiation shielding and kinetic penetrators. Tungsten carbide powder, especially fused tungsten carbide powder, is essential for cutting tools and wear parts. Global players like Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation dominate this space, with tungsten powder price per kg often exceeding $50 for high-purity grades.
7. Safety, Handling, and Misconceptions
Contrary to popular belief, not all titanium powders are pyrophoric—but fine titanium metal powder can ignite spontaneously in air, especially when dry and dispersed. Always store in inert atmospheres and follow OSHA guidelines for combustible dust. Also, titanium dioxide powder (TiO2) is generally safe in consumer products, though nano-sized versions are under regulatory review.
And no—powdered sugar’s whiteness comes from TiO2, but that’s unrelated to metallic titanium powder used in engineering. Similarly, you cannot ‘powder coat’ titanium in the traditional sense; instead, titanium parts may receive ceramic or plasma-sprayed coatings.
8. Conclusion
Titanium powder is far more than a raw material—it’s a gateway to next-generation manufacturing. With prices influenced by global supply chains and technological demand, staying informed about types like Ti64 powder, TiB2 powder, and spherical titanium powder is crucial. Whether you’re sourcing for additive manufacturing or exploring advanced ceramics, understanding the distinctions between titanium metal powder, TiO2 powder, and related compounds like molybdenum and tungsten powders ensures smarter decisions. As export regulations tighten and 3D printing expands, titanium powder will only grow in strategic value.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as 10. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
