1. Introduction
Just 24 hours ago, NASA announced a breakthrough in its collaboration with private aerospace firms to 3D print lightweight, high-strength rocket engine components using titanium powder—specifically gas-atomized Ti6Al4V powder. This milestone underscores how titanium powder is no longer just a lab curiosity but a mission-critical material in next-gen engineering.

While many associate titanium with aircraft frames or hip implants, few realize that the real innovation lies in its powdered form. From pure titanium powder to advanced blends like titanium diboride powder, these materials are enabling unprecedented design freedom, weight savings, and biocompatibility.
2. Why Titanium Powder? The Rise of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing—commonly known as 3D printing—relies heavily on metal powders that can be precisely melted layer by layer. Titanium powder for 3D printing must meet strict criteria: high purity, spherical morphology, and consistent particle size distribution.
Among the most widely used is Ti6Al4V powder (also called Ti64 powder), a titanium alloy powder composed of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. It offers an exceptional strength-to-density ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility—making it ideal for both jet turbines and orthopedic implants.

- Gas atomized titanium powder is preferred for laser-based 3D printing due to its smooth, spherical shape, which ensures excellent flowability.
- HDH titanium powder (Hydride-Dehydride) is cheaper but irregular in shape, limiting its use to less demanding applications.
3. Titanium Powder Uses Beyond the Obvious
While titanium powder for 3D printing dominates headlines, niche applications are equally fascinating. For instance, titanium nitride powder and titanium carbide powder are used as hard coatings to enhance tool durability. Titanium diboride powder (TiB2) serves in armor composites and cathodes for aluminum smelting due to its extreme hardness and electrical conductivity.
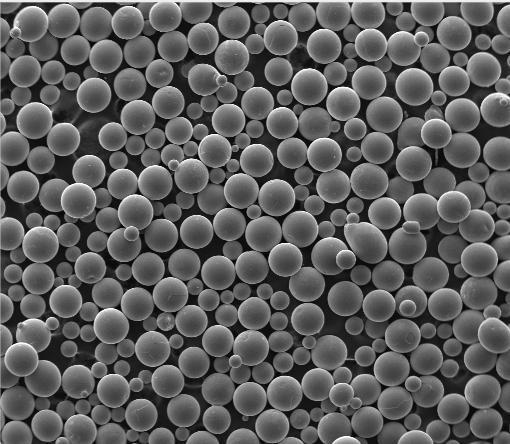
In contrast, TiO2 nano powder (titanium dioxide nanopowder) finds use in sunscreens and photocatalysts—but that’s a different beast from metallic titanium powder. Confusing the two is common, but they serve entirely different purposes.
Even more exotic is titanium flash powder, used in pyrotechnics, though it’s highly reactive and not related to industrial or medical-grade titanium metal powder.
4. Pricing and Sourcing: What’s Driving the Cost?
The titanium powder price per kg varies widely based on form, purity, and processing method. As of mid-2024, spherical titanium powder for 3D printing costs between $300–$600/kg, while Ti6Al4V powder price can exceed $500/kg for aerospace-grade material.
Factors influencing titanium powder cost include:
- Purity level (pure titanium powder vs. alloyed)
- Particle size distribution (narrow ranges command premium pricing)
- Production method (gas atomization is more expensive than HDH)
- Global supply chain constraints
Many engineers ask: ‘Is titanium powder cheaper than titanium wire?’ Generally, no—powder is more expensive due to complex production and handling requirements. However, in additive manufacturing, the material savings and design efficiency often justify the higher titanium metal powder price.
5. Suppliers and Procurement Considerations
When you buy titanium powder, choosing a reliable titanium powder supplier is crucial. Leading vendors offer certified gas atomized titanium powder with traceable chemistry and particle analysis. International titanium powder suppliers often comply with ASTM or ISO standards for additive manufacturing.
Similarly, those seeking molybdenum powder or tungsten powder for high-temperature applications must vet suppliers carefully. Molybdenum disulfide powder (MoS2 powder) and tungsten disulfide powder (WS2 powder) are solid lubricants, while spherical tungsten powder is used in radiation shielding and kinetic penetrators.
Note: While titanium powder for sale is increasingly accessible, always verify if the material is suitable for your intended process—especially if you’re exploring titanium powder additive manufacturing.
6. Safety and Handling: Don’t Treat It Like Ordinary Dust
Titanium dust is flammable and can be pyrophoric in fine particle form—meaning it may ignite spontaneously in air. Proper handling under inert atmospheres (argon or nitrogen) is essential during printing and post-processing.
This is why facilities using titanium 3D printing powder invest heavily in explosion-proof equipment and strict safety protocols. Never confuse industrial titanium powder with cosmetic TiO2 powder—despite the similar names, their risks and regulations differ vastly.
7. The Bigger Picture: Titanium Among Refractory Metal Powders
Titanium isn’t alone in the advanced powder arena. Molybdenum metal powder and tungsten metal powder are also critical in extreme environments. Molybdenum powder uses include furnace components and aerospace alloys, while tungsten powder density (19.25 g/cm³) makes it ideal for counterweights and armor.
Companies like Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation supply high-density tungsten powder and fused tungsten carbide powder for wear-resistant coatings. Meanwhile, TZM powder (a molybdenum alloy) offers enhanced strength at high temperatures.
Yet titanium remains unmatched for applications requiring light weight, strength, and biocompatibility—especially when processed via modern additive techniques.
8. Conclusion
From NASA’s latest rocket nozzles to patient-specific spinal implants, titanium powder—particularly Ti64 and spherical titanium powder—is enabling engineering feats once deemed impossible. While the titanium powder price per kg remains high, its value in performance-critical applications continues to grow.
As additive manufacturing scales and recycling methods improve, expect broader access to titanium powder for 3D printing. For now, partnering with a trusted titanium powder supplier and understanding material specifications are key to unlocking its full potential.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as Titanium. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
