1. Introduction
When you think of cutting-edge manufacturing, 3D printing might come to mind—but not all 3D printing is created equal. In high-stakes industries like aerospace and biomedical engineering, the magic lies not just in the printer, but in the material: titanium powder. Specifically engineered for precision, strength, and biocompatibility, titanium powder has become the go-to feedstock for additive manufacturing of mission-critical components.
From jet engine brackets to custom hip implants, titanium powder enables parts that are lighter, stronger, and more complex than traditional methods allow. But not all titanium powders are the same—and understanding the nuances of types like Ti6Al4V powder, pure titanium powder, and even specialty variants like titanium diboride powder is essential for engineers, buyers, and innovators alike.
2. Why Titanium Powder Dominates Advanced 3D Printing
2.1. The Rise of Titanium Powder for 3D Printing
Titanium powder for 3D printing has surged in popularity due to its exceptional strength-to-density ratio, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with human tissue. Unlike steel or aluminum, titanium maintains performance under extreme temperatures and stresses—making it ideal for aerospace applications. In medicine, its biocompatibility allows for permanent implants without rejection.
The most widely used alloy is Ti6Al4V (also called Ti64), a titanium alloy powder composed of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. This formulation offers the perfect balance of weldability, fatigue resistance, and manufacturability in powder bed fusion processes like selective laser melting (SLM).
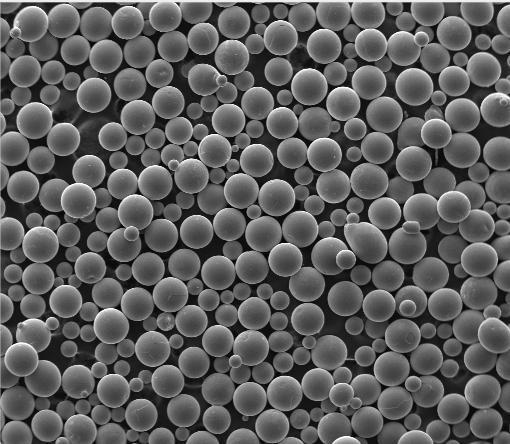
2.2. Powder Morphology Matters: Spherical vs. HDH
Not all titanium metal powder is suitable for 3D printing. For consistent layer deposition and high packing density, manufacturers prefer spherical titanium powder—typically produced via gas atomization. Gas atomized titanium powder flows smoothly, ensuring uniform melt pools and defect-free parts.

In contrast, HDH (Hydride-Dehydride) titanium powder is angular and cheaper but less ideal for high-precision additive manufacturing. It’s often used in pressing and sintering rather than laser-based 3D printing.
3. Pricing and Sourcing: What Drives Titanium Powder Cost?
3.1. Understanding Titanium Powder Price Per Kg
The titanium powder price per kg varies widely—typically from $100 to over $500—depending on purity, particle size distribution, morphology, and alloy type. Ti6Al4V powder price is generally higher than pure titanium powder due to the added alloying elements and stricter quality controls.
Factors influencing titanium powder cost include production method (gas atomized vs. plasma rotating electrode), oxygen content, and certification requirements (e.g., ASTM F3049 for medical use). The titanium powder for 3D printing price also reflects global supply chain dynamics and raw material availability.
3.2. Where to Buy Titanium Powder
Reputable titanium powder suppliers include international players like AP&C (a GE Additive company), Carpenter Additive, and TLS Technik. When you buy titanium powder, ensure it meets industry standards for flowability, particle size (typically 15–45 µm for SLM), and low contamination levels.

Buyers should also consider alternatives like titanium nitride powder or titanium carbide powder for wear-resistant coatings, though these are not used as primary feedstocks in structural 3D printing.
4. Beyond Titanium: How Molybdenum and Tungsten Powders Compare
4.1. Molybdenum Powder in High-Temperature Applications
While titanium dominates lightweight, high-strength applications, molybdenum powder shines where extreme heat resistance is needed. Molybdenum metal powder and alloys like TZM powder are used in furnace components, rocket nozzles, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Molybdenum disulfide powder (MoS2 powder) serves as a dry lubricant, and its price is significantly lower than titanium powder. However, moly powder lacks titanium’s corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, limiting its use in medical fields.
4.2. Tungsten Powder for Density and Radiation Shielding
Tungsten powder, especially high density tungsten powder and spherical tungsten powder, is prized for its unmatched density (19.25 g/cm³) and radiation absorption. Tungsten carbide powder is common in cutting tools, while pure tungsten powder finds use in counterweights and shielding.
Though tungsten powder price per kg can rival or exceed titanium in some grades, its brittleness and high melting point make it less suitable for complex 3D-printed geometries. Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation and Tungco are key tungsten powder suppliers.
5. Specialty Titanium Powders and Emerging Uses
Beyond standard Ti64, niche variants are gaining traction:
- Titanium diboride powder (TiB2 powder) and titanium boride powder enhance hardness in metal matrix composites.
- TiH2 powder (titanium hydride) is used as a foaming agent in metal foam production.
- TiO2 nano powder and titanium nanopowder serve in catalysis and sensors—not structural printing.
- Titanium coated diamond powder improves thermal conductivity in electronic substrates.
Note: Titanium flash powder and burnt titanium powder coat are unrelated to industrial additive manufacturing and often refer to pyrotechnic or surface treatment contexts.
6. Conclusion
Titanium powder—especially in the form of spherical, gas-atomized Ti6Al4V—is the cornerstone of high-performance additive manufacturing in aerospace and medical sectors. While titanium powder price per kg remains a consideration, the performance benefits justify the investment for critical applications. As 3D printing technology advances, demand for certified, high-quality titanium 3D printing powder will only grow. Whether you’re sourcing from an international titanium powder supplier or comparing it to molybdenum or tungsten alternatives, understanding the specific properties and uses of each powder type is key to success in advanced manufacturing.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as Titanium. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
