1. Introduction
In the past 48 hours, the additive manufacturing sector has seen renewed interest in high-performance metal powders following a major aerospace supplier’s announcement of a new certification for Ti6Al4V powder in jet engine components. This spotlight on titanium powder underscores its growing role in cutting-edge industries—from medical implants to defense systems.

Titanium powder isn’t just one material—it’s a family of powders with distinct chemistries, morphologies, and price points. Whether you’re exploring titanium powder for 3D printing, evaluating titanium powder price per kg, or comparing it to alternatives like molybdenum powder or tungsten powder, understanding these differences is critical. Let’s break down the seven most important types of titanium powder and how they stack up.
2. Pure Titanium Powder vs. Titanium Alloy Powder
Pure titanium powder (often Grade 1 or 2) is prized for its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. It’s commonly used in chemical processing and medical devices. However, it lacks the strength needed for structural aerospace parts.
Enter titanium alloy powder—especially Ti6Al4V (also called Ti64 powder), which contains 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. This alloy dominates the titanium powder for 3D printing market due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance. Ti6Al4V powder price typically runs 20–30% higher than pure titanium metal powder price, but the performance payoff justifies the cost in demanding applications.
3. Production Methods: Gas Atomized vs. HDH Titanium Powder
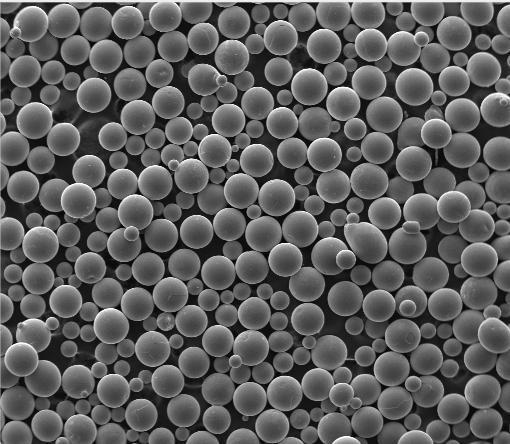
How titanium powder is made dramatically affects its shape, flowability, and suitability for additive manufacturing. Gas atomized titanium powder produces spherical particles ideal for consistent powder bed fusion in 3D printing. This morphology ensures smooth spreading and high packing density—key for titanium powder additive manufacturing.

In contrast, HDH (Hydride-Dehydride) titanium powder yields irregular, angular particles. While cheaper, HDH powder is better suited for pressing and sintering rather than high-end 3D printing. Consequently, spherical titanium powder commands a premium—often reflected in the titanium powder for 3d printing price.
4. Specialty Titanium Compounds: Beyond Metal Powders
Not all ‘titanium powders’ are metallic. TiO2 powder (titanium dioxide powder), especially in nano form (TiO2 nano powder), is widely used in sunscreens, paints, and food—not for structural use but for UV blocking and whitening.
Then there are advanced ceramics like titanium nitride powder, titanium carbide powder, and titanium diboride powder (TiB2 powder). These ultra-hard, high-melting-point materials serve in cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings, and even as reinforcements in metal matrix composites. Titanium diboride price remains high due to complex synthesis, but demand is rising in armor and electronics.
5. Titanium Powder Pricing and Sourcing Trends
Titanium powder price per kg varies wildly: pure titanium powder might cost $80–$150/kg, while certified Ti6Al4V powder for aerospace 3D printing can exceed $300/kg. Factors like purity, particle size distribution, and supplier certification (e.g., ASTM F3049) heavily influence cost.
When you buy titanium powder, always verify if it’s from a reputable titanium powder supplier with traceable quality control. Beware of misleading terms like ‘titanium flash powder’—which refers to pyrotechnic mixtures, not industrial-grade material—and ‘burnt titanium powder coat,’ which isn’t a standard powder form at all.
6. How Titanium Compares to Molybdenum and Tungsten Powders
While titanium dominates lightweight applications, refractory metals like molybdenum powder and tungsten powder fill high-temperature niches. Molybdenum metal powder (including MoS2 powder and TZM powder) excels in furnace components and lubrication, with molybdenum disulfide powder uses spanning from aerospace greases to nanoelectronics.
Tungsten powder, especially spherical tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder, offers extreme density and hardness. Tungsten powder price per kg often exceeds titanium’s, but its unmatched wear resistance makes it ideal for cutting tools and radiation shielding. Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation remains a key player in this space.
7. Safety, Handling, and Common Misconceptions
Titanium dust can be flammable under certain conditions—fine titanium powder is sometimes pyrophoric, especially in nanopowder form. Always handle with inert atmospheres and proper PPE.
Contrary to myths, titanium dioxide in powdered sugar is unrelated to industrial titanium metal powder. And no, you can’t effectively powder coat titanium—the oxide layer prevents adhesion, though ‘titanium coated diamond powder’ exists for abrasive applications.
8. Conclusion
Choosing the right titanium powder depends on your application: pure for biocompatibility, Ti64 for 3D printing strength, or ceramic variants like TiB2 for hardness. With titanium powder for sale from numerous international titanium powder suppliers, always prioritize certified, application-matched material. As additive manufacturing grows, expect innovations in recycling, pricing transparency, and hybrid powders—making now the perfect time to understand your options.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as 7. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
