1. Introduction
In the past 48 hours, global supply chain alerts have highlighted increased demand for spherical titanium powder due to a surge in aerospace and medical 3D printing projects, particularly involving Ti6Al4V alloy. With titanium powder price per kg fluctuating amid energy costs and export regulations, professionals across manufacturing sectors are seeking reliable guidance on procurement, safety, and application.

Titanium powder—also referred to as ti powder or titanium metal powder—is a critical material in high-performance industries. Whether you’re exploring titanium powder for 3d printing, evaluating titanium powder uses in coatings, or comparing titanium powder cost against alternatives like molybdenum powder or tungsten powder, this guide delivers actionable steps to navigate the landscape safely and effectively.
2. Understanding Titanium Powder Types and Applications
Not all titanium powders are the same. Key variants include:
- Pure titanium powder: Used in chemical processing and research.
- Ti6Al4V powder (also called ti64 powder): The most common titanium alloy powder for aerospace and biomedical 3D printing.
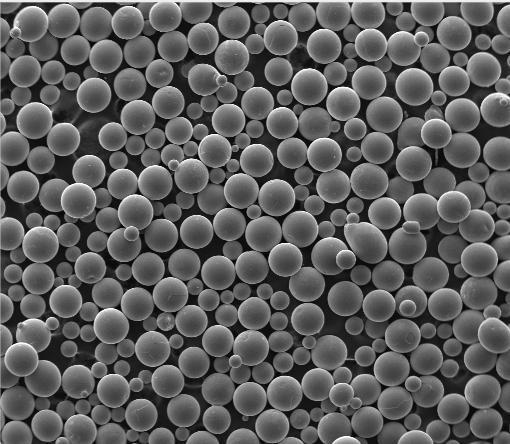
- Spherical titanium powder: Produced via gas atomization for optimal flow in additive manufacturing.
- HDH titanium powder: Made through hydride-dehydride processing; less expensive but irregular in shape.
- TiO2 nano powder and titanium dioxide powder: Used in cosmetics, sunscreens, and pigments—not for structural applications.
- Specialty powders like titanium nitride powder, titanium carbide powder, titanium diboride powder (TiB2), and titanium boride powder serve niche roles in cutting tools and wear-resistant coatings.
Avoid confusion with non-metallic forms: titanium flash powder is pyrotechnic, while burnt titanium powder coat refers to surface oxidation—not usable powder.
3. How to Safely Handle and Store Titanium Powder
Titanium dust is flammable and can be pyrophoric in fine particle form, especially under dry, oxygen-rich conditions.
Follow these safety protocols:
- Store in sealed, inert-atmosphere containers (argon or nitrogen).
- Keep away from ignition sources, moisture, and oxidizers.
- Use explosion-proof equipment in handling areas.
- Wear PPE: respirators, anti-static clothing, and eye protection.
Never mix titanium powder with chlorates or perchlorates—this creates highly unstable flash compositions.

4. Sourcing and Buying Titanium Powder
When you buy titanium powder, consider these factors:
- Purity and particle size distribution (critical for 3d printing titanium powder).
- Morphology: spherical vs. irregular (gas atomized titanium powder flows better in AM machines).
- Certification: ASTM or ISO standards for medical/aerospace grades.
Reputable titanium powder suppliers include international titanium powder producers in the U.S., Germany, and Japan. Always request a Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Compare titanium powder price per kg across vendors—but beware of unusually low ti powder price, which may indicate contamination or incorrect alloy grade (e.g., mislabeled Ti6Al4V powder). Current titanium powder for 3d printing price ranges from $300 to $800/kg depending on specification.
5. Titanium Powder in Additive Manufacturing
Titanium powder additive manufacturing relies on consistent powder characteristics:
- Use only spherical titanium powder with narrow size distribution (typically 15–45 µm).
- Recycle powder carefully: monitor oxygen content; discard if >1500 ppm.
- Ti6Al4V powder price reflects its dominance in medical implants and jet engine components.
Ensure your 3D printer supports reactive metals. Build chambers must maintain oxygen levels below 100 ppm to prevent embrittlement.
6. Common Problems and Solutions
Problem: Powder clumping during printing.
Solution: Dry the powder at 120°C under vacuum before use; verify humidity control in storage.
Problem: High titanium powder cost impacting project budgets.
Solution: Consider blending with lower-cost alloys or optimizing support structures to reduce waste.
Problem: Confusion between titanium dioxide powder and metallic titanium powder.
Solution: TiO2 powder is non-conductive and used in sunscreen—it cannot be used in 3D printing. Always verify CAS numbers.
7. Related Powders: Molybdenum and Tungsten
While sourcing titanium powder, you may encounter complementary refractory metal powders:
- Molybdenum powder (moly powder) and molybdenum disulfide powder (MoS2 powder) are used as dry lubricants and high-temp alloys.
- Tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder offer extreme density and hardness—ideal for radiation shielding and cutting tools.
Note: Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation and other tungsten powder suppliers often serve similar markets as titanium powder suppliers, but these materials are not interchangeable.
Do not substitute molybdenum metal powder or tungsten metal powder for titanium in AM without full process validation.
8. Conclusion
Successfully working with titanium powder requires attention to safety, specification accuracy, and supplier reliability. Whether you’re procuring pure titanium powder, Ti6Al4V powder for medical devices, or evaluating titanium powder for sale from international vendors, always prioritize certified, application-appropriate grades. With proper handling and informed purchasing—guided by up-to-date titanium metal powder price trends—you can leverage this advanced material safely and efficiently in cutting-edge manufacturing.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as How. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
