1. Introduction
Titanium powder might sound niche, but it’s quietly revolutionizing industries from aerospace to medical implants. Lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant, titanium in powdered form unlocks advanced manufacturing techniques—especially additive manufacturing (3D printing). Whether you’re an engineer, researcher, or procurement specialist, understanding the nuances of titanium powder—including types like pure titanium powder, ti6al4v powder, and even exotic variants like titanium nitride powder—is essential for making informed decisions.

2. What Is Titanium Powder?
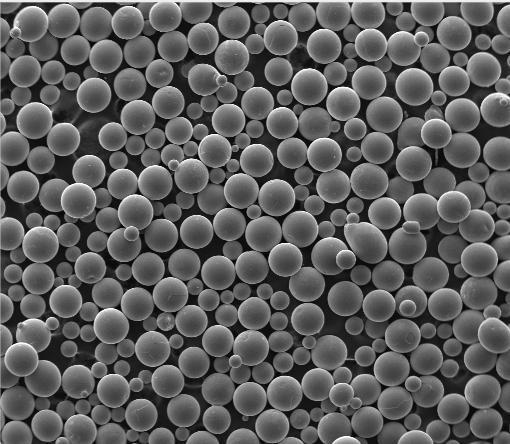
Titanium powder refers to finely divided particles of titanium metal or its compounds. It comes in various forms: elemental titanium (often called ti powder or titanium metal powder), alloys (like ti64 powder), and ceramics (such as tio2 powder or titanium carbide powder). Particle size, shape (spherical vs. irregular), and purity dramatically affect performance. For instance, spherical titanium powder is preferred for 3D printing due to better flowability, while hdh titanium powder (produced via hydride-dehydride process) is common for lower-cost applications.
3. How Is Titanium Powder Made?
The two dominant production methods are gas atomization and the HDH process. Gas atomized titanium powder yields spherical particles ideal for high-end uses like aerospace components. In contrast, HDH titanium powder is more angular and economical, often used in powder metallurgy. Other specialized forms include tih2 powder (titanium hydride), which decomposes to fine titanium dust during processing, and burnt titanium powder coat residues from surface treatments.
4. Key Types and Variants
- Pure titanium powder: Used where biocompatibility or corrosion resistance is critical.
- Ti6Al4V powder (also called ti64 powder): The most widely used titanium alloy powder, especially in medical and aerospace 3D printing.
- Tio2 nano powder: A white pigment in cosmetics and sunscreens—not metallic, but chemically related.
- Titanium nitride powder and titanium carbide powder: Hard, wear-resistant ceramics for coatings and cutting tools.
- Titanium diboride powder (tib2 powder) and titanium boride powder: Ultra-hard materials for armor and refractory applications.
- Titanium flash powder: A pyrotechnic mix—highly reactive and not used industrially.
- Titanium coated diamond powder: Used in precision polishing and grinding.
5. Titanium Powder Uses
Titanium powder uses span multiple high-tech fields. In additive manufacturing, titanium powder for 3d printing enables complex, lightweight parts for jet engines and patient-specific implants. Beyond that, it’s used in powder metallurgy to make gears and bearings, in pyrotechnics (though rarely), and as a catalyst support in chemical processes. Ti6al4v powder dominates the 3d printing titanium powder market due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility.
6. Pricing and Cost Factors
The titanium powder price varies widely based on purity, particle size, morphology, and volume. On average, titanium powder price per kg ranges from $100 to over $500. Ti6al4v powder price tends to be higher than pure titanium powder due to alloying elements. Similarly, 3d printing titanium powder price reflects stringent quality controls—spherical, gas atomized grades command premium rates. When you see ‘titanium powder cost’ quoted online, always check if it includes certification, packaging, and shipping.
7. Where to Buy and Supplier Considerations
When you want to buy titanium powder, choosing a reputable titanium powder supplier is crucial. Look for suppliers offering certified material data sheets, consistent particle size distribution, and experience with your application—whether it’s biomedical, aerospace, or research. International titanium powder vendors often serve global markets, but local suppliers may offer faster turnaround. Always verify if the product is truly suitable for your intended use—e.g., titanium powder for sale labeled ‘for research only’ may not meet ASTM standards for medical devices.
8. Related Industrial Powders: Molybdenum and Tungsten
While titanium powder gets attention, molybdenum and tungsten powders are equally vital in high-temp and wear-resistant applications. Molybdenum powder (moly powder) includes variants like molybdenum disulfide powder (mos2 powder)—a dry lubricant—and tzm powder for furnace parts. Similarly, tungsten powder (wolfram powder) is prized for its density and melting point. Global tungsten & powders corporation and other suppliers offer spherical tungsten powder, tungsten carbide powder, and ws2 powder. Though unrelated chemically, these materials often appear alongside titanium in advanced manufacturing contexts.
9. Safety and Handling
Fine titanium dust can be flammable or even pyrophoric under certain conditions—always handle in inert atmospheres when possible. Store away from oxidizers, and follow OSHA guidelines for metal powders. Unlike tio2 powder (generally safe in consumer products), elemental titanium powder requires industrial-grade safety protocols.
10. Conclusion
From enabling next-gen 3D printed implants to powering cutting-edge aerospace components, titanium powder is far more than just ground-up metal. Understanding the differences between gas atomized titanium powder and HDH variants, knowing current titanium powder price trends, and selecting the right titanium powder supplier can make or break your project. Whether you’re exploring titanium powder for sale for prototyping or large-scale production, this versatile material continues to push the boundaries of modern engineering.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as Titanium. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
