1. Introduction
In the past 48 hours, global supply chain updates from major additive manufacturing hubs have highlighted increased demand for spherical titanium powder due to expanded aerospace production using titanium powder additive manufacturing. With this surge, professionals across industries—from medical device manufacturers to defense contractors—are seeking reliable guidance on sourcing, handling, and applying titanium-based powders effectively and safely.

Titanium powder—often referred to as ti powder—is a critical material in high-performance sectors. Whether you’re exploring titanium powder for 3d printing, metallurgy, or surface coatings, understanding its properties, safety protocols, and market dynamics is essential. This guide delivers actionable steps to navigate these complexities.
2. Understanding Types of Titanium Powder
Not all titanium powders are the same. Selecting the correct variant depends on your application:
- Pure titanium powder: Used in chemical processing and biocompatible implants.
- Ti6Al4v powder (also called ti64 powder): The most common titanium alloy powder, ideal for aerospace and medical 3D printing.
- Spherical titanium powder: Produced via gas atomization for optimal flow in additive manufacturing.
- HDH titanium powder: Made through hydride-dehydride processing; cost-effective but irregular in shape.
- Specialty powders: Includes titanium nitride powder, titanium carbide powder, titanium diboride powder (TiB2), and titanium boride powder—used in cutting tools and wear-resistant coatings.
Note that tio2 powder (titanium dioxide) and tio2 nano powder are chemically distinct from metallic titanium powders and serve roles in pigments, sunscreens, and photocatalysis—not structural applications.
3. How to Safely Handle Titanium Dust and Powder

Titanium metal powder is highly reactive in fine form and can be pyrophoric—meaning it may ignite spontaneously in air, especially if particle size is below 45 microns. Follow these safety steps:
- Always store in sealed, inert-atmosphere containers (argon or nitrogen).
- Use explosion-proof equipment in processing areas.
- Wear anti-static clothing, gloves, and respirators rated for metal dust.
- Never use water to extinguish titanium powder fires; Class D fire extinguishers are required.
Avoid confusion with burnt titanium powder coat residues, which are oxides and generally stable—but still require proper disposal per local regulations.
4. Sourcing and Pricing Considerations
When you buy titanium powder, price varies significantly based on purity, morphology, and alloy composition. Key pricing benchmarks include:
- Titanium powder price per kg for pure grades: $80–$200/kg.
- Ti6al4v powder price: $150–$350/kg, depending on sphericity and oxygen content.
- 3d printing titanium powder price typically commands a premium due to stringent quality controls.
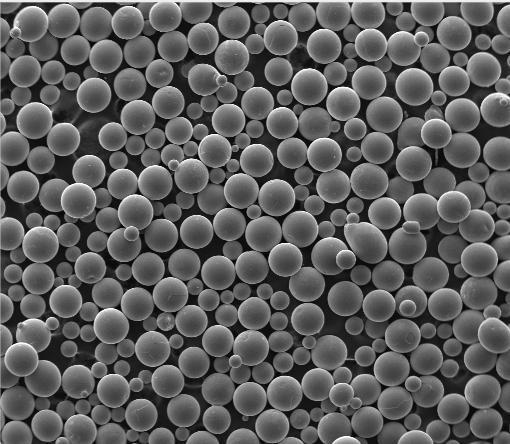
Compare quotes from reputable titanium powder suppliers offering certified material data sheets (MDS). Be wary of unusually low titanium powder cost—it may indicate contamination or incorrect particle size distribution.
Also note that international titanium powder shipments may require export licenses due to dual-use regulations.
5. Common Applications and Material Selection
Choosing the right titanium powder depends on your end use:
- For additive manufacturing: Use gas atomized titanium powder with high sphericity and low oxygen (<1000 ppm). Ti64 powder is standard for load-bearing parts.
- For metal injection molding (MIM): HDH titanium powder offers cost efficiency.
- For thermal spray or composite reinforcement: Consider titanium carbide powder or titanium diboride powder for hardness and thermal stability.
Do not substitute tio2 powder or titanium flash powder (a pyrotechnic mix) in structural applications—they lack metallic integrity.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Users often encounter these problems—and solutions:
- Poor powder flow in 3D printers: Caused by irregular particle shape. Switch to spherical titanium powder.
- High porosity in printed parts: Likely due to moisture absorption. Dry powder at 150°C under vacuum before use.
- Unexpected oxidation during sintering: Ensure furnace atmosphere is properly controlled (argon or high-vacuum).
- Difficulty removing powder from complex geometries: Use ultrasonic cleaning with inert solvents, never water.
7. Related Powders: When Molybdenum or Tungsten May Be Better Choices
In high-temperature or wear-intensive environments, alternatives like molybdenum powder or tungsten powder might outperform titanium:
- Molybdenum metal powder (including tzm powder and molybdenum disulfide powder) excels above 1000°C.
- Tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder offer superior density and abrasion resistance—ideal for drilling tools and radiation shielding.
Global tungsten & powders corporation and other tungsten powder suppliers provide high-density tungsten powder for specialized uses. Compare molybdenum powder price and tungsten powder price per kg against titanium metal powder price to assess total lifecycle value.
8. Conclusion
Successfully working with titanium powder requires attention to material grade, safety, and supplier credibility. Whether you’re using titanium powder for 3d printing, metallurgy, or advanced composites, aligning your selection with technical requirements—and staying informed on real-time market trends—ensures performance, safety, and cost efficiency. Always verify certifications, handle with extreme caution, and consult experts when scaling production.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as How. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
