1. Introduction
In the past 48 hours, global additive manufacturing firms have reported a surge in demand for titanium powder for 3d printing, driven by aerospace and medical implant innovations. With this spike, questions about safety, pricing, and material selection are more urgent than ever.

Whether you’re an engineer, hobbyist, or procurement specialist, knowing how to properly handle, store, and buy titanium powder is essential. Mistakes can lead to fire hazards, wasted investment, or failed prints. This guide gives you actionable steps to navigate the complex world of titanium metal powder safely and cost-effectively.
2. Understand the Different Types of Titanium Powder
Not all titanium powder is the same. Choosing the wrong type can ruin your project or pose serious risks.
- Pure titanium powder: Used in chemical processing and research. Less common in 3D printing.
- Ti6Al4V powder (also called Ti64 powder): The most widely used titanium alloy powder for aerospace and medical 3d printing.
- Spherical titanium powder: Ideal for additive manufacturing due to excellent flowability.
- HDH titanium powder (Hydride-Dehydride): Irregular shape, lower cost, used in pressing and sintering.
- Gas atomized titanium powder: High-purity, spherical particles—premium choice for critical 3D printing applications.
- TiO2 powder and TiO2 nano powder: Not metallic; used in sunscreens, paints, and ceramics—not for printing or metallurgy.
- Titanium nitride powder, titanium carbide powder, titanium diboride powder (TiB2), and titanium boride powder: Hard, ceramic-like materials for coatings and composites.
- Titanium flash powder and burnt titanium powder coat: Highly reactive—avoid unless you’re trained in pyrotechnics.
3. Safety First: Handling Titanium Dust
Titanium powder is flammable—and fine titanium dust can be pyrophoric (ignites spontaneously in air).
Always work in a well-ventilated area with explosion-proof equipment. Never use open flames or sparks nearby.
Wear PPE: Nitrile gloves, safety goggles, and a NIOSH-approved respirator rated for metal dust.
Store in sealed, inert containers (argon or nitrogen-filled) away from oxidizers like molybdenum trioxide powder or tungsten oxide powder.
Never mix titanium powder with chlorates or perchlorates—this creates extremely sensitive explosive mixtures.
4. How to Buy Titanium Powder Without Overpaying
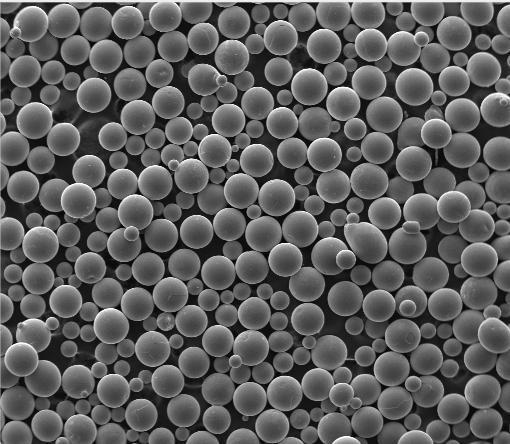
Titanium powder price varies wildly based on purity, particle size, shape, and alloy.
Check these key pricing benchmarks:
- Titanium powder price per kg: $100–$500+ for standard grades.
- Ti6Al4V powder price: Typically $300–$800/kg for spherical, gas-atomized powder suitable for 3D printing.
- 3D printing titanium powder price: Expect to pay a premium for certified, low-oxygen (<600 ppm) batches.
- Ti powder price vs. titanium metal powder price: Often used interchangeably, but confirm if it’s pure Ti or an alloy.
Compare quotes from multiple titanium powder suppliers. Reputable vendors include international titanium powder producers with ISO certifications.
Beware of unusually low prices—they may indicate contaminated or non-spherical powder unsuitable for additive manufacturing.
5. Storage and Shelf Life Best Practices
Store titanium powder in a cool, dry place in airtight containers under argon or vacuum.
Label all containers clearly: Include alloy type (e.g., Ti64 powder), particle size (e.g., 15–45 µm), and date received.
Avoid long-term storage near molybdenum powder, tungsten powder, or other reactive metal powders—even if sealed, cross-contamination risks exist during handling.
Inspect powder before use: Clumping, discoloration, or odor may indicate oxidation or moisture absorption.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid

Don’t assume all ‘titanium powder for sale’ is suitable for 3D printing. Only spherical, low-oxygen titanium 3d printing powder works reliably in laser powder bed fusion.
Don’t confuse titanium dioxide powder (TiO2) with metallic titanium powder—they serve completely different purposes.
Don’t store titanium powder next to tungsten carbide powder or molybdenum disulfide powder without proper segregation—dust mixing can create unpredictable reactions.
Don’t ignore MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets). Always review them before purchasing or using any metal powder, including dry moly powder or wolfram powder.
7. Where to Buy Reliable Titanium Powder
Look for suppliers that provide certificates of analysis (CoA) showing oxygen content, particle size distribution, and morphology.
Reputable sources include specialized metal powder vendors and global suppliers like those offering international titanium powder with traceable batch records.
For small-scale projects, some labs sell sample kits of pure titanium powder or Ti6Al4V powder—but verify their handling protocols.
If you’re also sourcing molybdenum powder or tungsten powder, consider consolidated procurement from vendors like Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation to reduce shipping risks and costs.
8. Conclusion
Titanium powder is a powerful material—but only when handled correctly. Whether you’re using it for additive manufacturing, research, or industrial coatings, understanding the differences between ti powder types, respecting safety protocols, and choosing the right supplier can save time, money, and prevent accidents. Always prioritize certified, spherical titanium powder for 3D printing, and never compromise on storage or handling. With the right approach, titanium powder can unlock incredible innovation in your work.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as How. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
