1. Introduction
In the past 48 hours, global additive manufacturing markets have seen a surge in demand for high-purity spherical titanium powder, driven by aerospace firms accelerating production of lightweight components amid supply chain shifts. With titanium powder at the heart of innovations in 3D printing, metallurgy, and advanced coatings, knowing how to properly handle, select, and purchase it is more critical than ever.

Whether you’re an engineer sourcing ti6al4v powder for aerospace parts, a researcher working with tio2 nano powder, or a hobbyist exploring titanium flash powder, this guide gives you actionable steps to navigate the complex world of titanium metal powder safely and cost-effectively.
2. Understanding Titanium Powder Types and Uses
Not all titanium powder is the same. The right type depends on your application:
- Pure titanium powder: Used in chemical processing and medical implants due to its biocompatibility.
- Ti6Al4V powder (also called ti64 powder): The most common titanium alloy powder, ideal for titanium powder additive manufacturing in aerospace and biomedical sectors.
- Spherical titanium powder: Produced via gas atomization, this flowable form is essential for consistent layering in 3D printing.
- HDH titanium powder (Hydride-Dehydride): Irregular-shaped, lower-cost option often used in powder metallurgy but less suitable for high-end 3D printing.
- Titanium nitride powder and titanium carbide powder: Hard, wear-resistant ceramics used in cutting tools and coatings.
- Titanium diboride powder (TiB2) and titanium boride powder: High-melting-point compounds used in armor and refractory applications.
Other niche forms include tih2 powder (titanium hydride), titanium nanopowder, and even titanium-coated diamond powder for specialized polishing.
3. Safety First: Handling Titanium Dust and Reactive Powders

Titanium powder—especially fine grades—is highly reactive and can be pyrophoric (ignites spontaneously in air). Always follow these safety protocols:
- Work in a well-ventilated area or inert atmosphere (argon/nitrogen glovebox) when handling fine ti powder.
- Avoid sparks, open flames, or static electricity near titanium dust.
- Store in sealed, non-reactive containers away from oxidizers.
- Never use water to extinguish titanium fires—it can worsen combustion. Use Class D fire extinguishers instead.
Note: Burnt titanium powder coat residues should be treated as hazardous waste and disposed of per local regulations.
4. How to Choose the Right Titanium Powder for 3D Printing
If you’re using titanium powder for 3d printing, focus on these key specs:
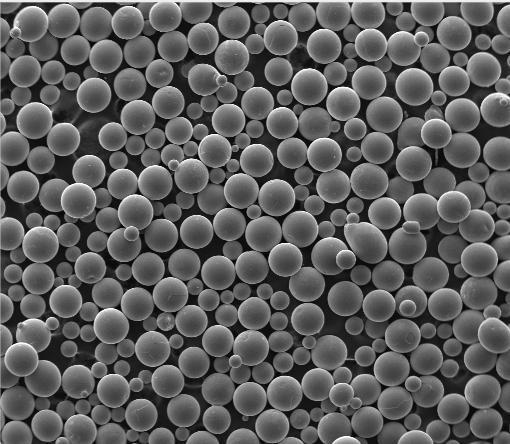
- Particle size distribution: Typically 15–45 microns for laser powder bed fusion.
- Sphericity: >90% spherical particles ensure smooth powder flow.
- Oxygen content: Should be <0.15% for aerospace-grade ti6al4v powder.
- Certification: Look for ASTM F3049 or ISO/ASTM 52900 compliance.
Gas atomized titanium powder is preferred over HDH for high-performance applications due to superior flowability and density.
5. Where and How to Buy Titanium Powder
When you buy titanium powder, prioritize reputable titanium powder suppliers who provide full material certifications. Consider these tips:
- Compare titanium powder price per kg across vendors—but don’t sacrifice quality for low cost.
- Request samples before bulk orders, especially for critical uses like medical or aerospace.
- Check if the supplier offers international titanium powder shipping and complies with export controls (titanium powder is regulated under ITAR/EAR in some cases).
Current market rates (as of mid-2024):
- Pure titanium powder: $80–$150/kg
- Ti6Al4V powder price: $150–$300/kg
- 3D printing titanium powder price varies based on purity and morphology—spherical grades cost more.
Always verify if the listing includes ‘titanium powder for sale’ with clear specs—not just generic ‘titanium dust’.
6. Related Powders: Molybdenum and Tungsten Options
Many projects involving titanium powder also require complementary refractory metals. Here’s a quick reference:
- Molybdenum powder (moly powder): Used in high-temp furnaces; molybdenum disulfide powder (MoS2 powder) serves as a dry lubricant.
- Tungsten powder: Extremely dense (19.3 g/cm³); pure tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder are common in wear parts and cutting tools.
Like titanium, both require careful handling—tungsten dust and tungsten carbide dust pose inhalation risks. Reputable sources include Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation and other certified tungsten powder suppliers.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Assuming all ‘titanium powder’ is suitable for 3D printing (HDH won’t work well in most printers).
- Ignoring oxygen content—high O2 levels embrittle printed parts.
- Confusing titanium dioxide powder (TiO2 powder, used in sunscreens and paints) with reactive titanium metal powder.
- Overlooking shipping restrictions—some countries restrict titanium powder exports due to dual-use concerns.
8. Conclusion
Titanium powder is a versatile but demanding material. Whether you’re investing in titanium powder for 3d printing, researching tio2 nano powder, or comparing titanium powder cost against alternatives like molybdenum or tungsten powders, always prioritize safety, certification, and supplier reliability. With the right approach, you’ll unlock the full potential of this remarkable material—without the risks.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as How. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
