1. Introduction
Titanium powder—often referred to simply as ti powder—is far more than just a fine metallic dust. This versatile material powers cutting-edge technologies from aerospace engineering to medical implants and additive manufacturing. With growing demand in high-performance industries, understanding what titanium powder is, how it’s made, and where to buy it has become essential for engineers, researchers, and manufacturers alike.
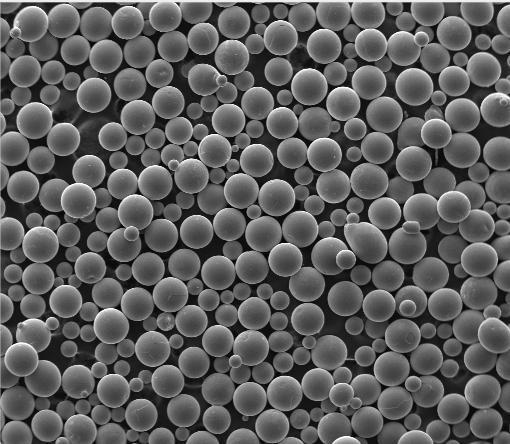
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about titanium powder: its different forms (including spherical titanium powder, HDH titanium powder, and gas atomized titanium powder), common uses, current market pricing, and trusted suppliers. We’ll also touch on related materials like molybdenum powder and tungsten powder for context.
2. What Is Titanium Powder?
Titanium powder is a finely divided form of titanium metal or its alloys. Unlike bulk titanium, which is known for its strength-to-density ratio and corrosion resistance, titanium powder enables advanced processing techniques like metal injection molding and, most notably, additive manufacturing (3D printing).
It’s important to distinguish between various types:
- Pure titanium powder: Used when high biocompatibility or corrosion resistance is needed.
- Titanium alloy powder: Such as ti6al4v powder (also called ti64 powder), the most widely used titanium alloy in aerospace and medical fields.
- Specialty powders: Including titanium nitride powder, titanium carbide powder, titanium diboride powder (TiB2 powder), and even titanium flash powder for pyrotechnics.
Note that tio2 powder (titanium dioxide powder) is chemically different—it’s an oxide used in paints, sunscreens, and food additives, not a metal powder for structural applications.
3. How Is Titanium Powder Made?
There are several industrial methods to produce titanium powder, each yielding different particle shapes, sizes, and purity levels:
3.1. Hydride-Dehydride (HDH) Process

The HDH method involves absorbing hydrogen into titanium sponge to make it brittle, then crushing and milling it into powder before removing the hydrogen. HDH titanium powder is cost-effective but often irregular in shape, making it less ideal for high-precision 3D printing.
3.2. Gas Atomization
Gas atomized titanium powder is created by melting titanium and spraying it with inert gas to form spherical particles. This spherical titanium powder flows better and is preferred for titanium powder additive manufacturing due to its consistent packing density and smooth layer deposition.
3.3. Plasma and Other Advanced Methods
Emerging techniques like plasma rotating electrode process (PREP) produce ultra-clean, spherical powders suitable for critical aerospace components.
4. Key Applications of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder uses span multiple high-tech sectors:
4.1. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
One of the fastest-growing markets is titanium powder for 3D printing. Aerospace companies use titanium 3d printing powder to create lightweight, complex parts, while medical device makers rely on it for custom implants. The demand has driven significant interest in titanium powder for 3d printing price trends, with costs varying based on alloy type and particle morphology.

4.2. Aerospace & Defense
Jet engines, airframes, and landing gear benefit from titanium alloy powder like ti6al4v powder due to its high strength and temperature resistance.
4.3. Medical Implants
Pure titanium powder and ti64 powder are biocompatible, making them ideal for hip replacements, dental implants, and surgical tools.
4.4. Other Uses
Less common but notable applications include titanium coated diamond powder for abrasives, burnt titanium powder coat for artistic finishes, and even tih2 powder as a hydrogen storage medium.
5. Pricing and Market Considerations
When looking to buy titanium powder, pricing depends heavily on form, purity, and production method. Here’s a general breakdown:
- Titanium powder price per kg for HDH-grade pure titanium powder may range from $50 to $150/kg.
- Spherical ti6al4v powder for 3D printing can cost $300–$800/kg, depending on certification and supplier.
- Specialty powders like titanium nanopowder or tio2 nano powder command premium prices due to their niche applications.
Factors influencing titanium powder cost include raw material availability, processing complexity, and global supply chain dynamics. International titanium powder markets are also affected by export regulations, especially for defense-related grades.
For those comparing materials, note that molybdenum powder and tungsten powder serve different purposes. Moly powder (molybdenum metal powder) is valued for high-temperature stability, while tungsten powder—especially spherical tungsten powder or fused tungsten carbide powder—is used in heavy alloys and wear-resistant coatings. Prices for tungsten powder price per kg and molybdenum powder price vary similarly based on purity and form.
6. Where to Buy Titanium Powder
Reputable titanium powder suppliers include both specialized metal producers and global distributors. When sourcing titanium powder for sale, consider:
- Certification (e.g., ASTM or ISO standards for additive manufacturing)
- Particle size distribution and morphology (spherical vs. irregular)
- Oxygen and nitrogen content (lower = higher quality for reactive applications)
Leading suppliers often provide technical data sheets and batch-specific testing. For industrial-scale needs, companies may also evaluate alternatives like molybdenum disulfide powder for lubrication or tungsten carbide powder for tooling—but these serve entirely different functions than titanium metal powder.
7. Safety and Handling Notes
While not as reactive as some metal powders, titanium dust can be flammable under certain conditions—especially fine or nanoparticle forms. Always store in inert atmospheres and follow OSHA guidelines for combustible dust. Titanium powder is not water-reactive like alkali metals, but oxidation can occur at high temperatures.
8. Conclusion
Titanium powder is a cornerstone material in modern advanced manufacturing. Whether you’re exploring titanium powder for 3d printing, seeking ti6al4v powder price quotes, or comparing it to other industrial powders like molybdenum or tungsten variants, understanding its properties, production methods, and market landscape is crucial. As additive manufacturing continues to grow, so too will innovation in titanium powder technology—making it a material worth watching closely.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as Titanium. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
