1. Introduction
Imagine a material so strong it can withstand jet-engine temperatures, so light it floats through engineering dreams, and so expensive it makes your wallet cry. Meet titanium powder—the unsung hero of modern manufacturing. Forget glitter; if you want real sparkle (and maybe a small fire hazard), titanium dust is where it’s at. From crafting hip implants to printing fighter jet parts layer by layer, titanium powder is quietly revolutionizing industries. And yes, before you ask—it’s not the same stuff in your powdered sugar (though both might give you a sugar rush… or a materials science degree).

2. What Exactly Is Titanium Powder?
Titanium powder—often abbreviated as Ti powder—is a fine particulate form of titanium metal. Don’t confuse it with titanium dioxide (TiO2) powder, the white pigment used in sunscreen and paint. Real titanium powder is reactive, metallic, and typically grayish-silver. Depending on how it’s made, it can be angular, spherical, nano-sized, or even pyrophoric (meaning it can ignite spontaneously in air—so maybe don’t try DIY fireworks with it).
- Pure titanium powder is elemental Ti, usually 99%+ pure.
- Titanium alloy powder includes blends like Ti6Al4v (also called Ti64), the superstar alloy used in medical and aerospace applications.
- Specialty variants include titanium nitride powder, titanium carbide powder, titanium diboride (TiB2) powder, and even titanium-coated diamond powder for ultra-hard composites.
3. How Is Titanium Powder Made?
Making titanium powder isn’t like grinding coffee beans. Two dominant methods rule the roost: HDH (Hydride-Dehydride) and gas atomization.
3.1 HDH Titanium Powder
HDH involves hydrogenating titanium sponge (yes, ‘sponge’—it’s porous and looks like a metallic kitchen scrubber), pulverizing it, then baking off the hydrogen. The result? Angular, cost-effective powder great for pressing and sintering—but not ideal for smooth-flowing 3D printing.
3.2 Gas Atomized Titanium Powder
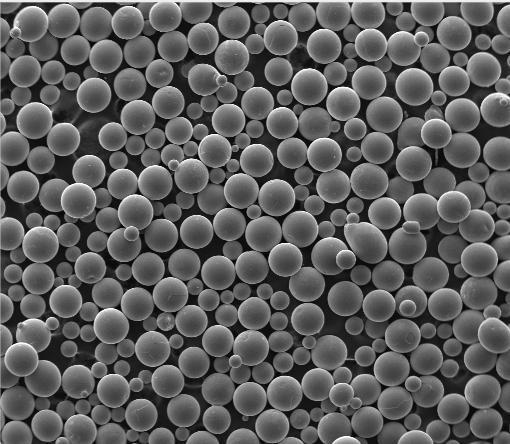
Gas atomization melts titanium and blasts it with inert gas (like argon), creating perfectly spherical particles. These flow like liquid sand and are the gold standard for titanium powder for 3D printing. Spherical titanium powder ensures consistent layering in additive manufacturing machines—critical when you’re printing a $500,000 jet engine bracket.
4. Titanium Powder Uses: Beyond Just Looking Cool
Titanium powder uses span far beyond novelty sparklers (though burnt titanium powder coat does make for dramatic YouTube videos).
- Aerospace: Jet engines, landing gear, and structural components benefit from titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio.
- Medical: Hip replacements and dental implants often use Ti6Al4v powder due to its biocompatibility.
- Additive Manufacturing: Titanium powder additive manufacturing is booming—especially with demand for lightweight, complex geometries.
- Pyrotechnics: Titanium flash powder creates brilliant white sparks (but please leave this to professionals—your garage isn’t a lab).
- Ceramics & Coatings: Titanium nitride powder gives that gold-like finish to drill bits; titanium carbide enhances wear resistance.
5. The Price Tag: Why Titanium Powder Costs So Much
Let’s talk numbers. Titanium powder price per kg can range from $100 to over $500, depending on purity, particle shape, and alloy type. Ti6Al4v powder price? Even higher. Titanium powder for 3D printing price reflects the precision needed—spherical, contaminant-free, and tightly controlled particle size distribution doesn’t come cheap.
Factors influencing titanium powder cost:

- Raw material scarcity (titanium ore isn’t rare, but refining it is energy-intensive).
- Production complexity (inert atmospheres, vacuum systems, strict quality control).
- Certification requirements (medical and aerospace grades need rigorous testing).
So, is titanium powder cheaper than titanium wire? Usually not—powder processing adds significant value, especially for advanced applications.
6. Where to Buy—and Who Supplies It
Looking to buy titanium powder? Reputable titanium powder suppliers include international players like VSMPO-AVISMA, Carpenter Technology, and AP&C (now part of GE Additive). Whether you need pure titanium powder, TiH2 powder (a hydrogenated precursor), or nano-sized TiO2 nano powder for research, always verify certifications and particle specs.
Pro tip: If a deal seems too good to be true—like ‘titanium powder for sale’ at $20/kg—it’s probably titanium dioxide or contaminated scrap. Buyer beware!
7. Bonus Round: Molybdenum and Tungsten Powders
While titanium steals the spotlight, its metallic cousins deserve mention. Molybdenum powder (moly powder) and tungsten powder are heavyweights in high-temp applications.
Molybdenum metal powder is used in furnace parts and electronics. Variants like molybdenum disulfide powder (MoS2 powder)—aka dry moly powder—are top-tier solid lubricants. Ferro molybdenum powder aids steelmaking, while TZM powder (titanium-zirconium-molybdenum) handles extreme heat.
Tungsten powder, denser than lead and nearly as hard as diamond, powers everything from filaments to armor-piercing rounds. Spherical tungsten powder enables advanced thermal spray coatings, and tungsten carbide powder is essential for cutting tools. Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation (often listed as Global Tungsten and Powder) is a major player here.
Like titanium, these powders aren’t cheap—tungsten powder price per kg hovers around $30–$80, while tungsten carbide powder price per kg can exceed $100. But when you need density, hardness, or heat resistance, there’s no substitute.
8. Conclusion
Titanium powder may look like unassuming gray dust, but it’s a powerhouse of modern engineering. Whether you’re printing aerospace parts, coating drill bits, or researching nanomaterials, understanding the nuances of Ti powder—from HDH vs. gas atomized forms to Ti64 vs. pure grades—is crucial. Yes, the titanium powder price stings, but for performance-critical applications, it’s worth every cent. Just remember: never confuse it with the TiO2 in your toothpaste… unless you enjoy metallic-flavored mint.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as Titanium. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
