1. Introduction
In a major development just 24 hours ago, NASA announced the successful test-firing of a liquid rocket engine component entirely fabricated using titanium powder-based additive manufacturing. The milestone underscores the growing reliance on titanium metal powder in mission-critical aerospace applications where strength-to-density ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability are non-negotiable.

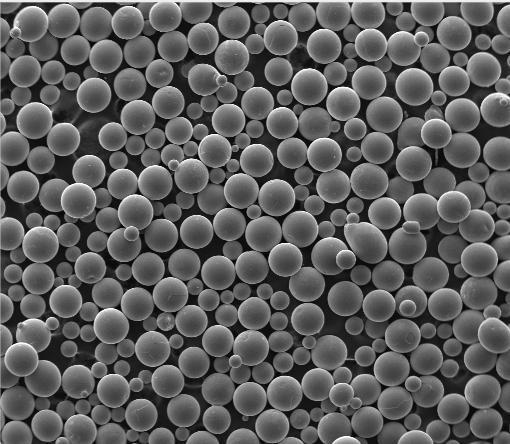
Titanium powder—especially in its spherical, gas-atomized form—is no longer a laboratory curiosity but a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing. From custom orthopedic implants to next-generation jet engines, this material enables geometries and performance unattainable through traditional methods.
2. Why Titanium Powder Dominates High-Performance 3D Printing
Additive manufacturing demands powders with consistent particle size, high sphericity, and low oxygen content. Gas atomized titanium powder meets these criteria, making it ideal for laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and electron beam melting (EBM) processes.
Among the most widely used variants is Ti6Al4v powder (also known as Ti64 powder), a titanium alloy powder composed of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. Its biocompatibility, fatigue resistance, and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures make it the gold standard for both aerospace and medical devices.
- Spherical titanium powder ensures smooth powder flow and dense part consolidation
- HDH titanium powder (Hydride-Dehydride) offers a lower-cost alternative but is less suitable for high-precision 3D printing
- Pure titanium powder is preferred for certain biomedical applications due to its inertness
3. Pricing and Procurement Considerations

The titanium powder price per kg varies significantly based on purity, morphology, and alloy composition. As of mid-2024, titanium powder for 3D printing price ranges from $300 to $800 per kg, with Ti6Al4V powder price typically hovering around $500/kg for aerospace-grade material.
Factors influencing titanium metal powder price include production method (gas atomization vs. plasma rotating electrode), certification requirements (AMS, ASTM), and batch volume. Buyers seeking to buy titanium powder should prioritize certified titanium powder suppliers who provide full traceability and powder characterization data.
While titanium powder cost remains high compared to steel or aluminum powders, its performance justifies the investment in weight-sensitive or life-critical applications. Those looking for titanium powder for sale must also consider ancillary costs like handling, storage (due to titanium dust flammability risks), and recycling infrastructure.
4. Niche Titanium-Based Powders and Their Roles
Beyond standard Ti64, specialized titanium powders serve ultra-niche functions:
- Titanium nitride powder and titanium carbide powder enhance surface hardness in coatings
- Titanium diboride powder (TiB2 powder) and titanium boride powder are used in composites for wear resistance
- TiO2 nano powder finds use in photocatalysis and UV-blocking applications—but is chemically distinct from metallic titanium powder
- Titanium flash powder, though pyrophoric and hazardous, is occasionally used in pyrotechnics (not recommended for industrial AM)
Note that burnt titanium powder coat residues require specialized cleaning protocols and should never be confused with functional additive manufacturing feedstock.
5. Comparative Context: Titanium vs. Molybdenum and Tungsten Powders
While titanium powder excels in lightweight, high-strength applications, other refractory metal powders serve complementary roles. Molybdenum powder (including TZM powder and molybdenum disulfide powder) offers superior high-temperature stability above 1,000°C, useful in furnace components and aerospace thrusters.
Similarly, tungsten powder—especially spherical tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder—is unmatched in density and wear resistance. Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation and other tungsten powder suppliers cater to industries requiring radiation shielding or cutting tools.
However, neither molybdenum metal powder nor tungsten metal powder matches titanium’s biocompatibility or specific strength. Thus, titanium 3D printing powder remains irreplaceable in human-implantable devices and fuel-efficient airframes.
6. Conclusion
Titanium powder for additive manufacturing represents the convergence of materials science and digital fabrication. With ongoing advances in powder production—such as improved gas atomized titanium powder consistency and reduced oxygen pickup—the titanium powder uses in aerospace, defense, and healthcare will only expand.
For engineers and procurement specialists, understanding the nuances between pure titanium powder, Ti6Al4V powder, and related compounds like TiH2 powder or titanium coated diamond powder is essential. As titanium powder price per kg gradually declines with scale, broader adoption across industrial sectors becomes increasingly viable.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as Unlock. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
