1. Introduction
In the past 48 hours, global demand for high-performance metal powders has surged due to expanded aerospace contracts involving next-generation jet engines and satellite components—many of which rely on titanium powder for lightweight, high-strength 3D-printed parts. This renewed interest highlights just how critical titanium powder has become in advanced manufacturing. But what exactly is titanium powder, and why are industries willing to pay premium prices for it?
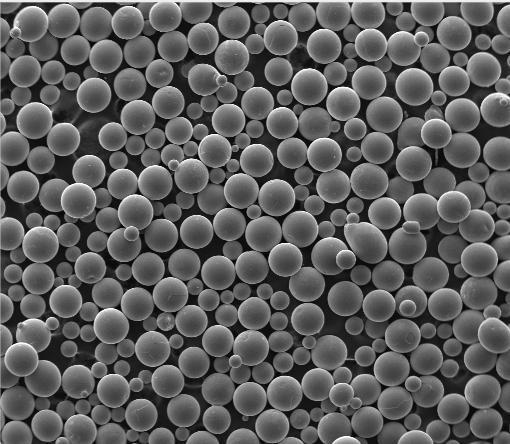
2. What Is Titanium Powder?
Titanium powder, often referred to simply as Ti powder, is a fine particulate form of titanium metal or its alloys. Unlike bulk titanium, which is known for its strength-to-density ratio and corrosion resistance, titanium powder unlocks unique processing capabilities—especially in powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing. It can appear as irregular particles (from HDH—Hydride-Dehydride processing) or highly spherical granules (from gas atomization), depending on the production method. While pure titanium powder is used in some applications, most industrial uses involve titanium alloy powder, such as the widely adopted Ti6Al4V (also called Ti64), which blends titanium with aluminum and vanadium for enhanced mechanical properties.
3. How Is Titanium Powder Made?
3.1. Gas Atomized Titanium Powder
Gas atomization involves melting titanium under vacuum or inert atmosphere and then disintegrating the molten stream with high-pressure argon or nitrogen gas. This yields spherical titanium powder ideal for 3D printing due to excellent flowability and packing density—key for consistent layer deposition in laser-based additive manufacturing systems.

3.2. HDH Titanium Powder
The Hydride-Dehydride (HDH) method produces irregularly shaped particles by first absorbing hydrogen into titanium sponge, making it brittle enough to crush into powder, then removing the hydrogen through vacuum heating. HDH titanium powder is less expensive than gas-atomized versions but is typically used in pressing-and-sintering applications rather than high-end 3D printing.
3.3. Other Forms
Specialty variants include titanium nitride powder (used in coatings), titanium carbide powder (for cutting tools), titanium diboride (TiB2) powder and titanium boride powder (for composites), and even titanium flash powder (a pyrotechnic mixture—not pure Ti). Note that TiO2 powder (titanium dioxide) and TiO2 nano powder are chemically distinct oxides used in pigments, sunscreens, and catalysts—not metallic titanium powder.
4. Key Uses of Titanium Powder

4.1. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
One of the fastest-growing applications is titanium powder for 3D printing. Aerospace, medical implants (like hip joints), and motorsports leverage titanium 3d printing powder to create complex, lightweight geometries impossible with traditional machining. Spherical titanium powder—especially Ti6Al4V powder—is the gold standard here. The titanium powder additive manufacturing market continues to expand as printers become more accessible and reliable.
4.2. Traditional Powder Metallurgy
Beyond 3D printing, titanium metal powder is pressed and sintered into filters, bearings, and structural components. Burnt titanium powder coat residues sometimes appear in post-processing but are generally removed during finishing.
4.3. Specialty Applications
Titanium nanopowder finds use in catalysis and sensors. Titanium coated diamond powder enhances abrasive performance. Meanwhile, TiH2 powder (titanium hydride) serves as a foaming agent in metal matrix composites.
5. Pricing and Market Considerations
Titanium powder price varies widely based on purity, particle size, morphology, and alloy type. Pure titanium powder might cost $100–$200 per kg, while high-quality spherical Ti6Al4V powder for 3D printing can exceed $400/kg. Factors influencing titanium powder price per kg include production method (gas atomized > HDH), certification requirements (e.g., ASTM standards), and order volume. Buyers often compare titanium powder cost against alternatives like molybdenum powder or tungsten powder—both used in high-temp applications but with different density and cost profiles.
6. Related Industrial Powders: Molybdenum and Tungsten
While titanium dominates lightweight applications, molybdenum powder (moly powder) and tungsten powder serve niche roles where extreme heat resistance or density is needed. Molybdenum metal powder, MoS2 powder (molybdenum disulfide powder), and TZM powder are common in furnace components and lubricants. Tungsten powder, especially spherical tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder, is prized for radiation shielding, cutting tools, and wear-resistant coatings. Global Tungsten & Powders Corporation and other suppliers offer these alongside titanium options, though tungsten powder price per kg often exceeds titanium’s due to raw material scarcity and processing complexity.
7. Safety and Handling
Fine titanium dust can be flammable or even pyrophoric under certain conditions—especially when dry and dispersed in air. Proper handling in inert atmospheres is essential. This contrasts with TiO2 powder, which is generally considered safe in consumer products (though nano-form debates continue). Always source from a reputable titanium powder supplier who provides safety data sheets and certified material.
8. Where to Buy
For those looking to buy titanium powder, numerous international titanium powder suppliers offer grades tailored to specific uses—from research-scale titanium nanopowder to industrial lots of Ti64 powder. When evaluating a titanium powder for sale listing, verify whether it’s gas atomized, HDH, or another type, and confirm compliance with relevant standards. Similarly, those needing molybdenum disulfide powder for sale or tungsten carbide powder for sale should prioritize certified vendors to ensure performance and safety.
9. Conclusion
Titanium powder is far more than just ground-up metal—it’s a gateway to revolutionary manufacturing techniques, especially in aerospace and healthcare. With prices ranging significantly based on form and application, understanding the differences between pure titanium powder, Ti6Al4V powder, and related compounds like TiO2 or TiB2 is crucial for informed purchasing. As additive manufacturing grows, so too will demand for high-quality, spherical titanium powder—making it a strategic material for the future of engineering.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as What. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
