1. Introduction
Just 48 hours ago, Relativity Space announced a major milestone: the successful hot-fire test of its fully 3D-printed Aeon R rocket engine, built almost entirely from titanium alloy powder. This breakthrough underscores a growing trend—titanium powder isn’t just a lab curiosity anymore. It’s fueling the next generation of aerospace innovation, medical breakthroughs, and even defense systems.

But what exactly is titanium powder used for beyond headlines? And why are engineers increasingly choosing ti powder over traditional metals? In this article, we’ll dive into the niche, high-value applications of titanium powder—especially in additive manufacturing—and unpack key considerations like titanium powder price, purity, and sourcing.
2. Titanium Powder in Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing (AM), or 3D printing, has revolutionized how complex metal parts are made—and titanium powder is at the heart of it. Unlike casting or machining, 3D printing with titanium metal powder allows for lightweight, high-strength components with intricate geometries that were previously impossible.
The most common material used is ti6al4v powder (also known as ti64 powder), a titanium alloy prized for its excellent strength-to-density ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. This makes it ideal for both jet engine brackets and patient-specific hip implants.
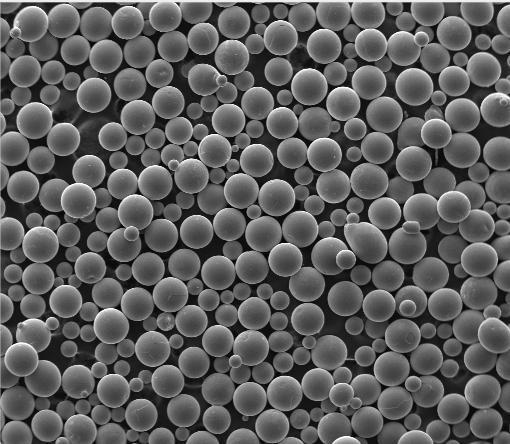
- Spherical titanium powder is preferred for laser-based 3D printing because its smooth shape ensures consistent flow and dense layer packing.
- Gas atomized titanium powder offers high purity and uniform particle size, critical for aerospace-grade reliability.
- HDH titanium powder (hydride-dehydride) is a lower-cost alternative but often requires post-processing for AM use.
3. Beyond Ti6Al4V: Specialty Titanium Powders
While ti6al4v dominates, other titanium-based powders serve ultra-niche roles:

Titanium nitride powder and titanium carbide powder are used as hard coatings or additives in cutting tools to boost wear resistance. Titanium diboride powder (or tib2 powder) and titanium boride powder enhance ceramic composites for armor and refractory applications.
For pyrotechnics or specialty ignition systems, titanium flash powder creates brilliant white sparks—but it’s highly reactive and not used in industrial AM. Meanwhile, tio2 nano powder (titanium dioxide nanopowder) finds use in sunscreens and photocatalysts, not structural printing.
Pure titanium powder is reserved for biomedical uses where alloying elements like aluminum or vanadium could pose biocompatibility risks. And for those wondering—yes, you can buy titanium powder specifically labeled for 3D printing, but quality varies widely by supplier.
4. Pricing and Sourcing Considerations
One of the biggest hurdles for new adopters is cost. Titanium powder price per kg can range from $100 to over $500, depending on grade, particle size, and production method. Ti6al4v powder price typically sits around $300–$450/kg, while 3d printing titanium powder price for aerospace-certified spherical grades can exceed $600/kg.
When you buy titanium powder, it’s essential to verify certifications, oxygen content, and flowability—especially if you’re using it for critical applications. Reputable titanium powder suppliers like Carpenter Additive, AP&C (a GE Additive company), and international titanium powder producers offer traceable, AM-ready materials.
Note: Titanium dust is flammable and requires careful handling—never confuse industrial-grade powder with pyrophoric forms used in fireworks.
5. How Titanium Compares to Molybdenum and Tungsten Powders
While titanium dominates lightweight AM, other refractory metal powders fill different roles. Molybdenum powder (moly powder) and molybdenum disulfide powder (mos2 powder) are used in high-temp furnaces and dry lubricants. Tungsten powder, with its extreme density and melting point, is favored for radiation shielding and kinetic penetrators.
Tungsten carbide powder and fused tungsten carbide powder excel in wear-resistant coatings, while global tungsten & powders corporation supplies high-density tungsten powder for defense and aerospace. However, these materials are far heavier and harder to print than titanium—making ti powder the go-to for weight-sensitive designs.
Interestingly, some hybrid applications combine titanium with tungsten or molybdenum powders for functionally graded materials, though this remains experimental.
6. Conclusion
From 3D-printed rocket engines to custom spinal implants, titanium powder is enabling technologies that were science fiction just a decade ago. Whether you’re evaluating titanium powder for sale for a startup or sourcing ti powder for research, understanding the differences between pure titanium powder, ti6al4v, and specialty variants like titanium diboride powder is crucial.
As additive manufacturing scales and recycling improves, titanium powder cost may drop—making it more accessible beyond elite aerospace and medical circles. Until then, partnering with a trusted titanium powder supplier and knowing your exact application needs will determine success.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as What. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
